Research
Diseases are caused by a complex interplay between different factors, such as genetics and the environment. A deeper understanding of the genetic risk factors of complex diseases can enable the development of more personalized treatments and prevention strategies.
Our research is focused on developing novel machine-learning methods to advance key computational aspects of precision medicine. We have a particular focus on the integration of genetic studies with relevant molecular patterns extracted from multi-omics data. For this, we aim to develop the next generation of methodologies that will consolidate large and heterogeneous sources of biomedical information to extract biological insight to ultimately improve human health.
Strongly committed to open source and open science, we use GitHub for the development of reproducible workflows and Manubot for the transparent authoring of modern and collaborative scholarly manuscripts.
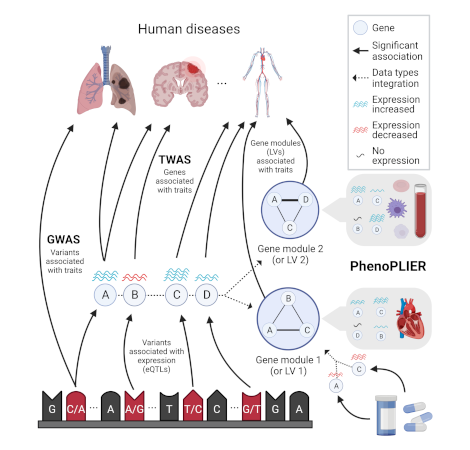
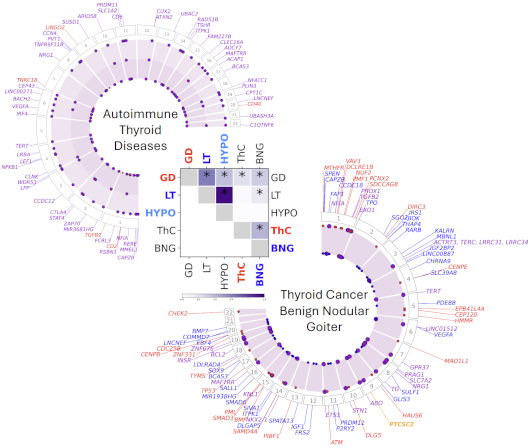
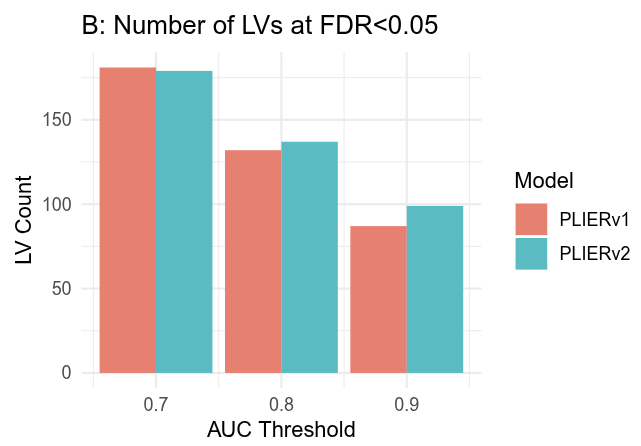
Integration of genetic studies with gene co-expression patterns
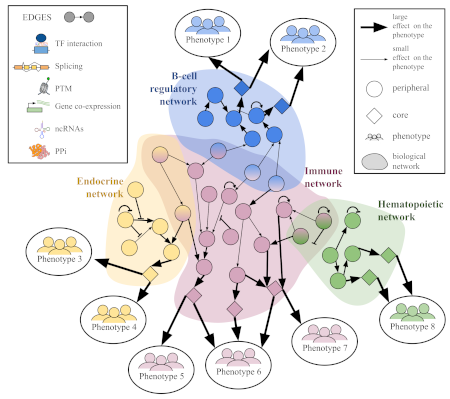
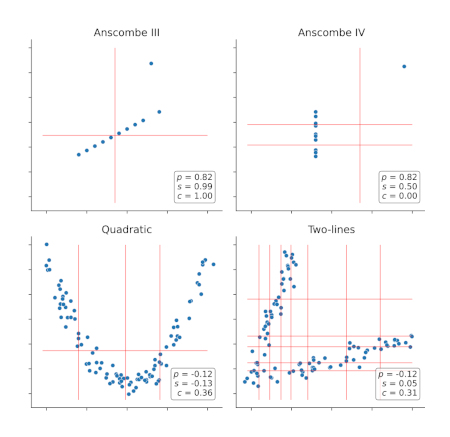
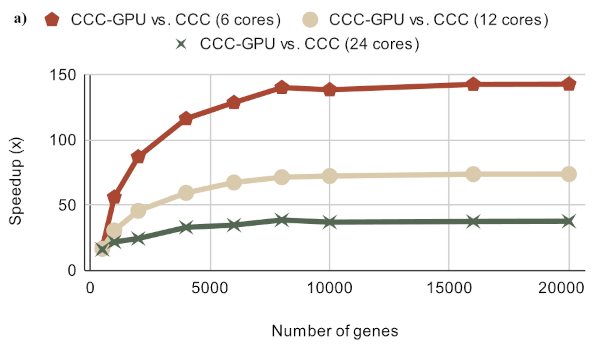
Extracting complex transcriptional signatures using not-only-linear correlation coefficients
Automatic revision of scholarly text using AI and large language models

All
2026

2025
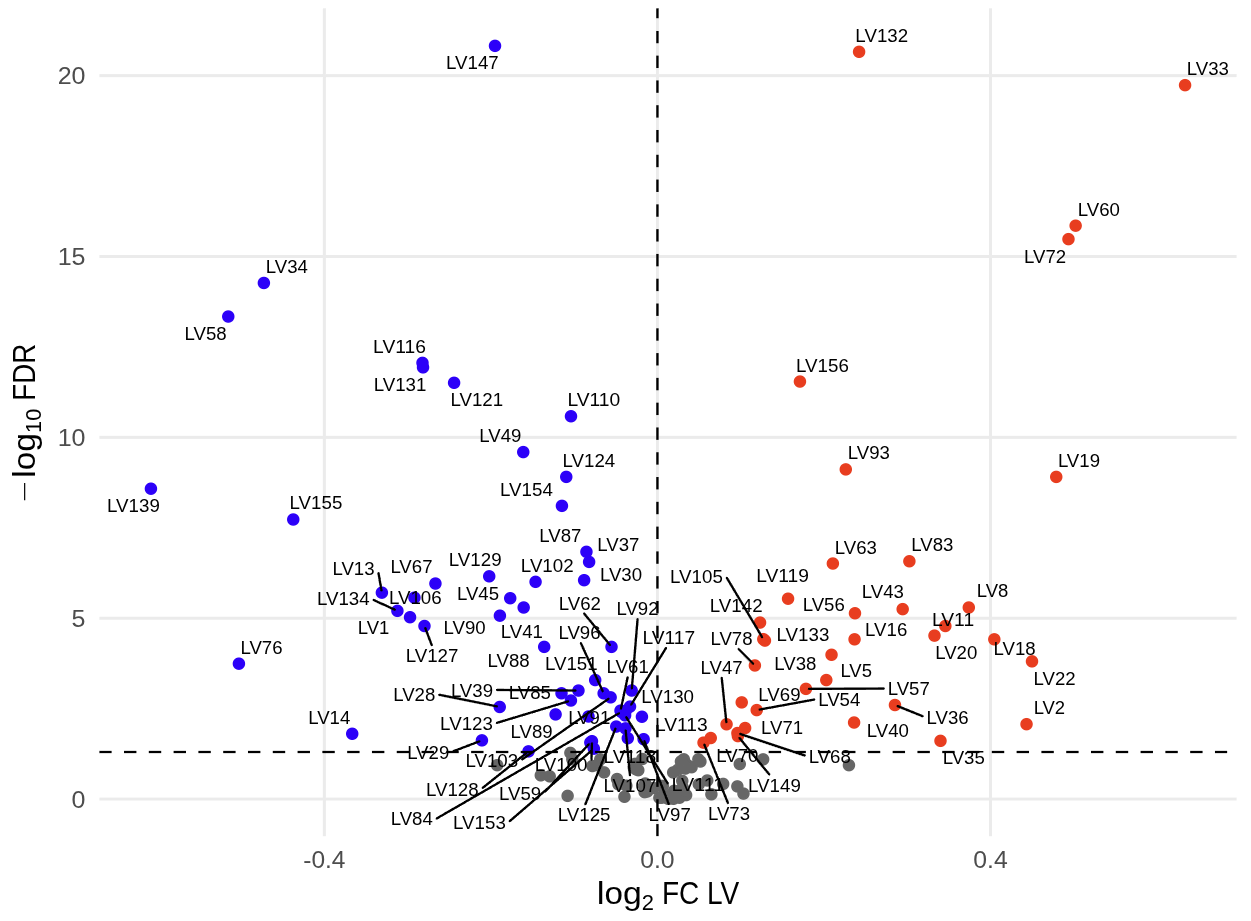
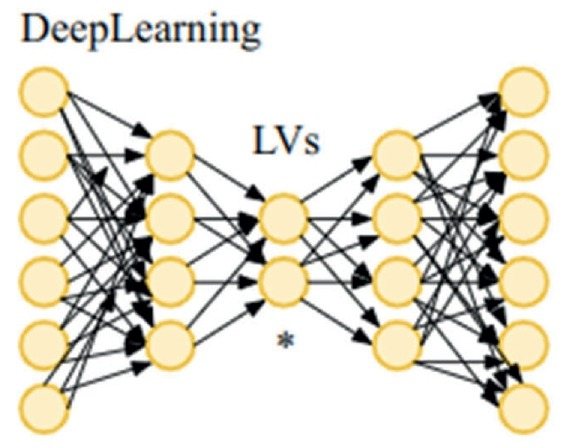

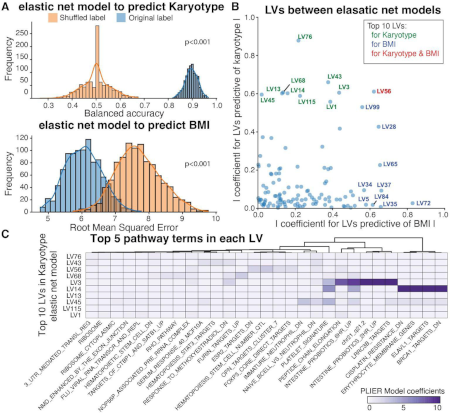
2024
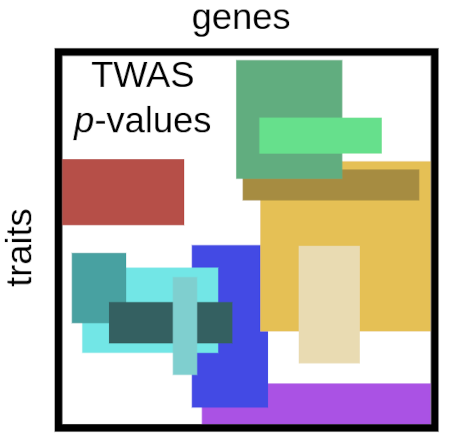



2023

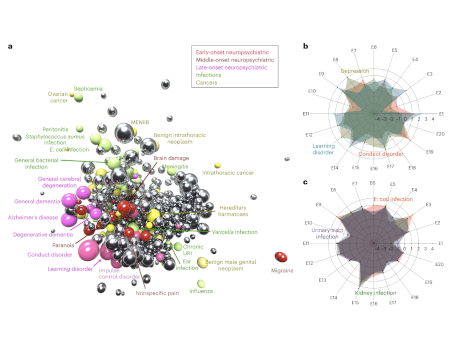
2022
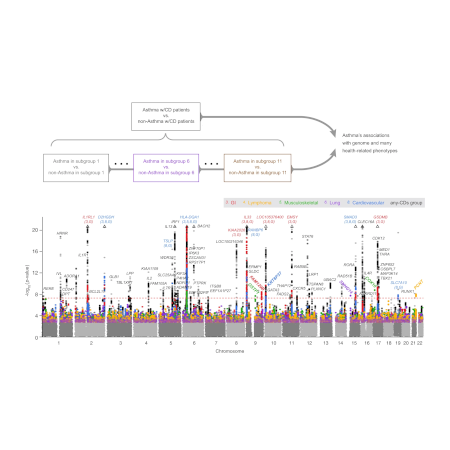
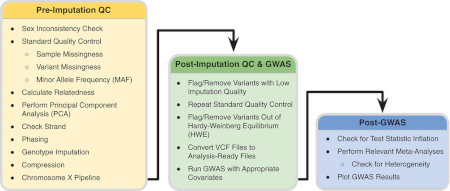
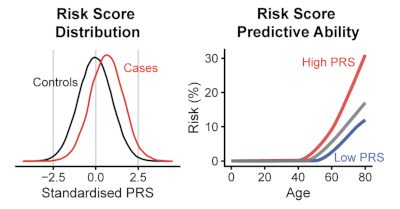
2021
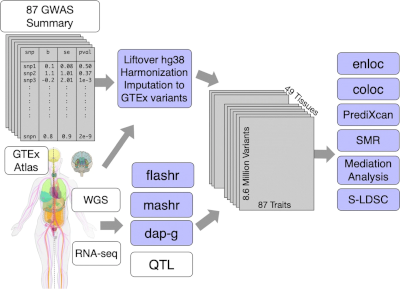
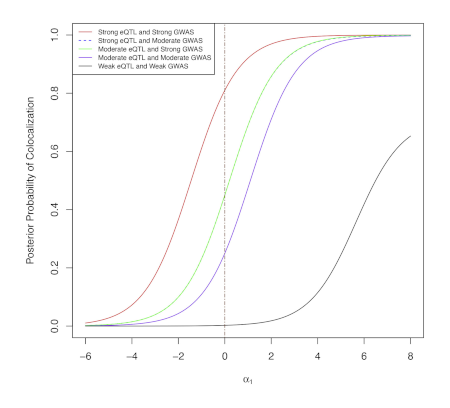
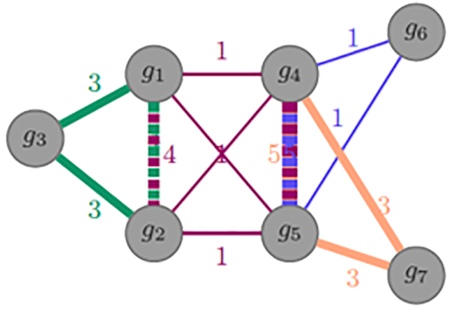
2020
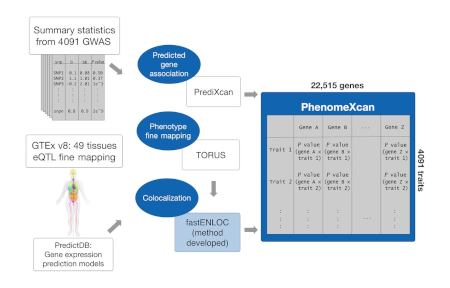
2019
2018
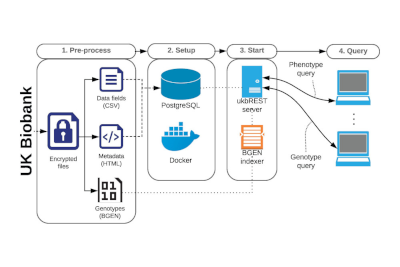
2016
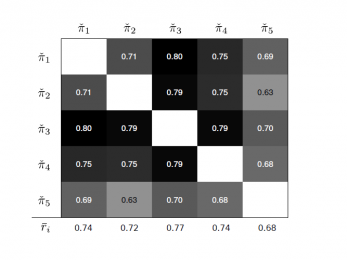
2015
2010